Categorization:Harness Component
With the continuous evolution of electronic devices towards thinness and miniaturization, both high-definition displays, camera modules, and 5G communication and high-speed data interfaces have put more stringent requirements on the signal performance and size design of cables. Among numerous cable solutions, extremely thin coaxial cables (Micro Coaxial Cable) stand out with their excellent signal integrity and superior anti-interference capabilities, becoming the "silent giant" in high-speed differential signal transmission. So, why can it stand out in complex high-speed transmission scenarios? Let's take a look together!
What is ultra-fine coaxial cable?
Micro coaxial cable is a super small diameter coaxial structure cable, with a common outer diameter of only 0.3mm~1.0mm. It consists of four parts: the inner conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer, and outer sheath. The structure is similar to that of traditional coaxial cables, but it excels in size and flexibility, enabling high-density wiring in narrow spaces.
What is differential signal?
Differential Signal is a method of transmitting equal-amplitude, opposite-phase electrical signals through two wires. At the receiving end, data is recovered by comparing the voltage difference between the two signal lines, rather than referencing the ground potential of a single signal line. This signal transmission method is commonly used in high-speed applications such as MIPI, USB 3.x, PCIe, SATA, DisplayPort, and automotive camera interfaces.
Its main advantages include:
Strong anti-interference capability
Good signal integrity
Suitable for high-speed, high-frequency signal transmission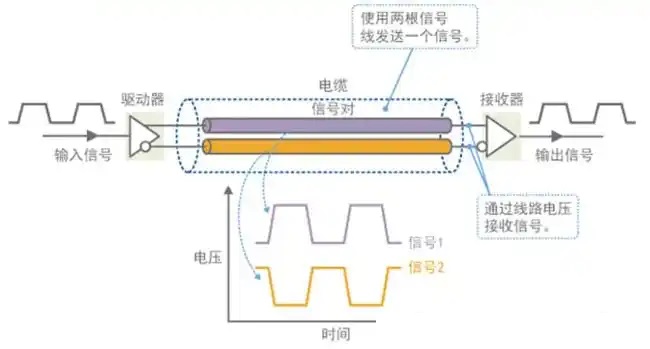
Why choose ultra-fine coaxial cable for high-speed differential signal transmission?
In high-speed signal transmission, common schemes include twisted pair (Twisted Pair) and very thin coaxial cable (Micro Coax).
But when a product追求 high density, small volume and ultra-high signal integrity, Micro Coax 显然 has more advantages.
The main reasons are as follows:
Precision Impedance Control
Extremely fine coaxial cables can strictly control the characteristic impedance of each conductor (commonly 50Ω or 100Ω differential), ensuring minimal reflection and standing waves during signal transmission, thereby reducing signal distortion.
Single-line independent shielding, stronger anti-interference
Each axis has an independent metallic woven or foil shielding layer, which can effectively isolate crosstalk between adjacent signals, maintaining high purity of differential signals.
High bandwidth, high-speed transmission capability
Micro Coax can support high-speed differential signal transmission of several GHz even more than 10Gbps, with low signal attenuation, low jitter, and stable and reliable transmission.
Flexible and suitable for compact spaces
Its excellent flexibility allows it to freely route in structures with extremely small internal spaces such as smartphones, laptops, VR devices, and vehicle-mounted cameras without losing performance.
With its comprehensive advantages such as precise impedance control, strong anti-interference ability, high bandwidth, and excellent flexibility, the ultra-thin coaxial cable (Micro Coaxial Cable) has become an ideal solution for high-speed differential signal transmission. It is widely used in products that have extremely high requirements for signal integrity and space utilization, and has become an indispensable key connection component in modern high-frequency electronic equipment.
We have long been focused on the design and customization of high-speed signal cables and extremely thin coaxial cables, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnection solutions. If you have any related needs or want to learn more, please contact: Manager Zhang.18913228573 (WeChat number).