Categorization:Harness Component

Conductor inside
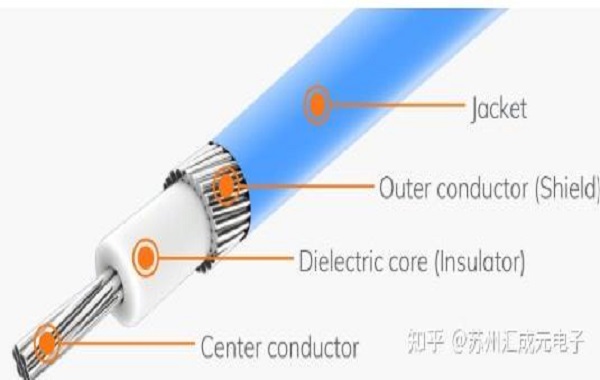
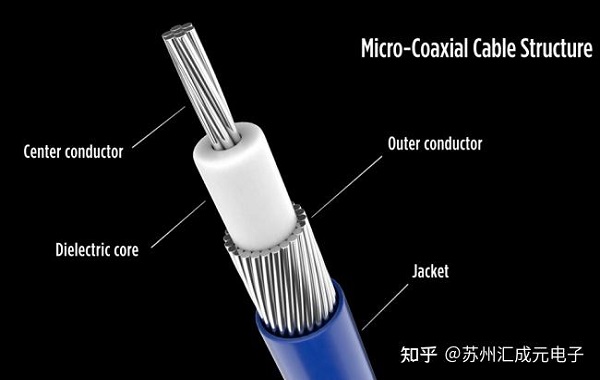
The inner conductor is located at the center of an extremely thin coaxial cable, usually made of silver-plated copper or tin-plated copper wire, used for transmitting electrical signals. It is like the main lane of an information highway, carrying all the signal traffic. The purity of the material and the surface treatment of the inner conductor directly affect the signal attenuation and transmission quality, which is the core of ensuring high-speed, low-loss transmission.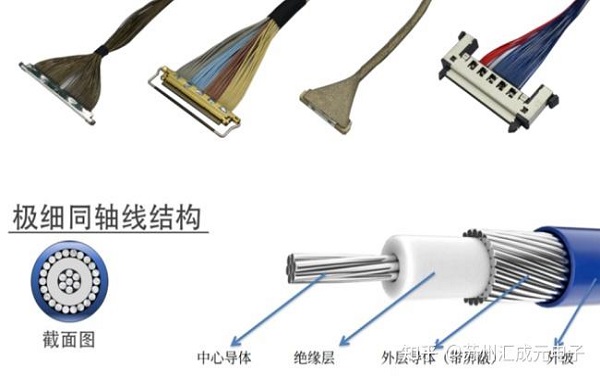
Insulation layer
The insulating layer is wrapped on the outer side of the inner conductor, and commonly used materials include high dielectric strength materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyethylene (PE). Its main function is to isolate the inner conductor from the shielding layer, prevent short circuits, and maintain a stable characteristic impedance, thus ensuring signal integrity. In high-speed signal transmission, the uniformity and stability of the insulating layer are crucial for transmission performance.
The shielding layer is a key factor in the anti-interference performance of ultra-fine coaxial cables. Usually, copper braided layer, aluminum foil layer, or multi-layer combined design is adopted to resist external electromagnetic interference (EMI) and prevent signal leakage. In applications with extremely high signal requirements, such as medical probes, camera modules, and AR/VR devices, the design of the shielding layer directly determines the stability and reliability of signal transmission.
I am[Suzhou Huichengyuan Electronic Technology]Long-term focus on the design and customization of high-speed signal cable harnesses and ultra-fine coaxial cable harnesses, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnect solutions. If you have related needs or want to learn more, please contact us:Manager Zhang 18913228573 (WeChat number the same)。