Categorization:Harness Component
As display technology rapidly advances to high-end specifications such as 8K, 120Hz, and HDR, HDMI 2.1 has become the key interface standard for high-speed video transmission. Its 48Gbps total bandwidth places extremely high requirements on the signal chain, and as a critical component in the transmission chain, the cable bundle directly affects signal integrity, anti-interference ability, and overall structural design. In the high-speed scenario of HDMI 2.1, engineers need to choose between traditional shielded twisted pair cables and extremely thin coaxial cable bundles.
This article will analyze why Micro Coaxial Cable is more suitable for HDMI 2.1 systems from aspects such as transmission characteristics, structural differences, and engineering practices.
High-speed transmission challenges of HDMI 2.1
HDMI 2.1 supports a bandwidth of 48Gbps, enabling uncompressed image output at 8K@60Hz and 4K@120Hz. At high frequencies over 10GHz, signal integrity, impedance consistency, EMI suppression, and crosstalk control become key design points. Especially in long cables, flexible wiring, or space-limited applications, the material, structure, and shielding method of the cable bundle will significantly affect link stability. This makes traditional cable solutions gradually face performance pressure under HDMI 2.1.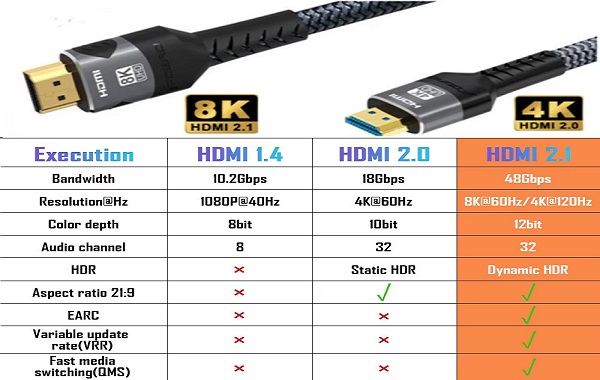
Two, the limitations of shielded twisted pair in high-speed applications
Twisted pair cables were widely used in the HDMI 1.4/2.0 era, with advantages such as light weight and low cost, but their weaknesses have become increasingly apparent under the 48Gbps specification, including difficulties in ensuring differential impedance consistency, increased high-frequency loss, insufficient crosstalk and EMI suppression, and especially in multi-channel parallel transmission, inter-channel coupling is more likely to lead to eye diagram collapse and intersymbol interference. Therefore, in HDMI 2.1 design, traditional twisted pair cables are no longer able to reliably support the stability of ultra-high bandwidth signals.
The advantages of extremely fine coaxial beam in HDMI 2.1
Extremely thin coaxial cable bundles use an independent coaxial structure composed of a central conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer, and sheath, with each core forming an independent shielding channel, naturally possessing precise impedance and excellent EMI suppression capability. In high-frequency transmission environments up to dozens of GHz, the coaxial structure can significantly reduce reflections, crosstalk, and losses, ensuring signal integrity. By using low dielectric constant insulation materials and silver-plated copper conductors, the transmission attenuation can be further reduced. At the same time, the flexible coaxial cables with a diameter of only 0.3~0.5mm are very suitable for compact devices, foldable wiring, 8K display modules, and high-speed image systems. This is also the core reason why high-end HDMI 2.1 data cables and embedded vision modules are increasingly inclined to adopt Micro Coax solutions.
The 48Gbps ultra-high-speed transmission in the HDMI 2.1 era is making traditional twisted pairs gradually show performance bottlenecks, while ultra-thin coaxial cable bundles, with their precise impedance, excellent EMI suppression, low loss at high frequencies, and flexible layout capabilities, are becoming the preferred solution for high-end video systems and embedded high-speed interfaces. As display technology continues to develop towards higher resolutions and higher refresh rates, Micro Coax will occupy a dominant position in more high-speed interconnect scenarios.
I am[Suzhou Huichengyuan Electronic Technology]Long-term focus on the design and customization of high-speed cable harnesses and ultra-thin coaxial cable harnesses, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnection solutions. For more information, please feel free to contactManager Zhang: 18913228573 (same number as WeChat)。