Categorization:Harness Component
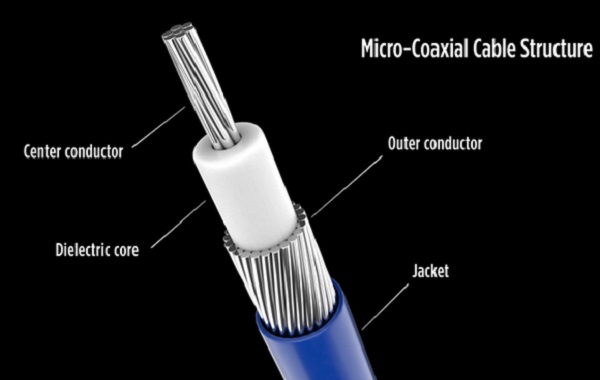
Part 1: Characteristics and Advantages of ultra-fine coaxial cables
Extremely thin coaxial cables are a type of miniature coaxial cable with a diameter usually ranging from 0.2mm to 0.5mm. They consist of an inner conductor, an insulating layer, a shielding layer, and an outer sheath, and have excellent shielding performance and signal integrity. They can achieve high-frequency, high-speed, and low-loss transmission within a limited space, with flexible wiring and reliable connections. They are suitable for internal use in precision electronic devices such as camera modules, display modules, AI servers, high-speed storage, and chip testing. In high-density, long-distance, or strong interference environments, extremely thin coaxial cables can maintain signal quality and ensure stable high-speed signal transmission.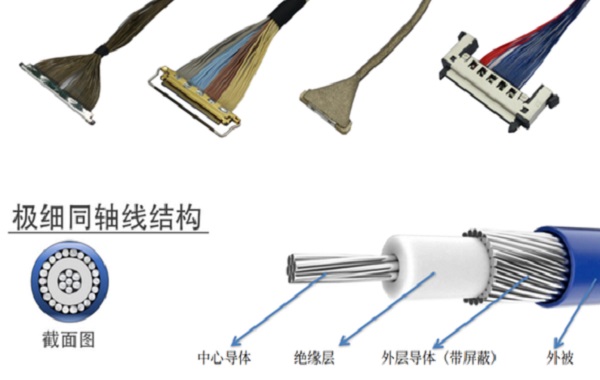
The characteristics and advantages of high-speed differential lines
High-speed differential lines are a wiring method based on PCB routing or twisted pair wiring, which transmit mutually inverted signals through two signal lines. The receiving end uses a differential amplifier to cancel out common-mode interference, thereby improving the noise immunity. Its wiring design is relatively flexible, with lower cost, and is widely used in medium and short-distance high-speed transmission, such as high-speed interfaces between the mainboard and the daughterboard, USB, HDMI, LVDS, and PCIe, and other consumer electronic devices. High-speed differential lines are suitable for scenarios that are sensitive to cost, have limited transmission distance, and are not seriously interfered by the environment.
Three, choice and application logic
The ultra-thin coaxial cables and high-speed differential lines are not simply a matter of good or bad, but a choice based on the application scenario. If the system needs to ensure signal integrity in high-density, long-distance, or strong interference environments, ultra-thin coaxial cables have more advantages; if the application is sensitive to cost, has a short transmission distance, and a good interference environment, high-speed differential lines are more suitable. Engineers need to consider various aspects such as signal integrity, spatial layout, environmental interference, and cost, in combination with specific requirements, in order to determine the optimal solution.