Categorization:Harness Component

Signal integrity and external interference risk
Extremely fine coaxial cable bundles are prone to electromagnetic interference from internal equipment such as robot motors, switch-mode power supplies, and wireless modules due to their small size and short transmission distance. These interferences can cause signal distortion, image frame loss, or bit errors, severely affecting the performance of the vision system. Therefore, ensuring signal integrity is the primary task of the design.
Comprehensive shielding and grounding design
360° metallic shielding is an effective anti-interference measure. It forms a Faraday cage by the outer shielding to prevent external electromagnetic signals from intruding and to prevent signal leakage within the wires. The shielding material can be foil, metal woven mesh, or a composite structure, taking into account both flexibility and shielding performance. The shielding layer needs to be reliably grounded at the equipment housing and adopt a multi-point grounding design to reduce common-mode interference and stabilize the electromagnetic environment of the system.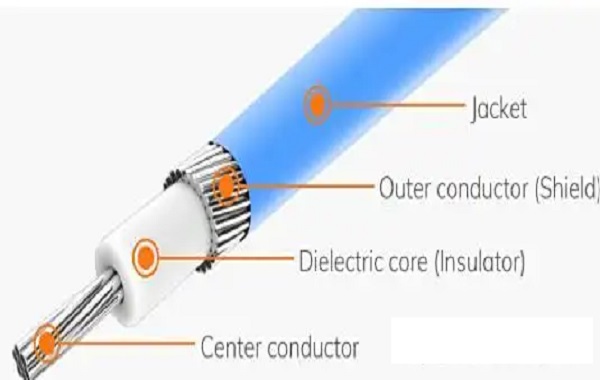
Three, bead filter and reasonable wiring
At the key nodes of the wiring harness, ferrite beads or filters can be installed to absorb high-frequency common-mode noise and provide an additional protective layer for the signal. At the same time, the wiring should be planned reasonably to avoid parallel or crossing with high-power power lines or servo motor lines, and the bending radius should be controlled to prevent mechanical stress from damaging the shielding integrity, ensuring signal stability.
Four, differential matching and verification testing
If the camera module uses differential signal transmission, it is necessary to ensure that the lengths of the P/N lines match to avoid internal delay causing electrical field asymmetry; good impedance matching can reduce reflection and crosstalk, enhancing transmission quality. The final design should be verified through EMC testing, spectrum analysis, and shielding effectiveness measurement to ensure that the extremely thin coaxial cable bundle can still achieve high-speed, low-error rate, and stable image transmission in complex electromagnetic environments.