In today's rapid development of AI, the speed and stability of signal transmission have become a key factor in system performance, whether it's autonomous driving, intelligent robots, or high-definition camera module groups. NVIDIA tends to recommend using extremely fine coaxial cables (Micro Coaxial Cable) rather than traditional FFC ribbon cables on its visual computing platforms like Jetson.
This article will analyze the reasons behind this choice from four perspectives: structure, electrical performance, mechanical characteristics, and practical applications, providing references for the design of high-speed interconnect solutions.
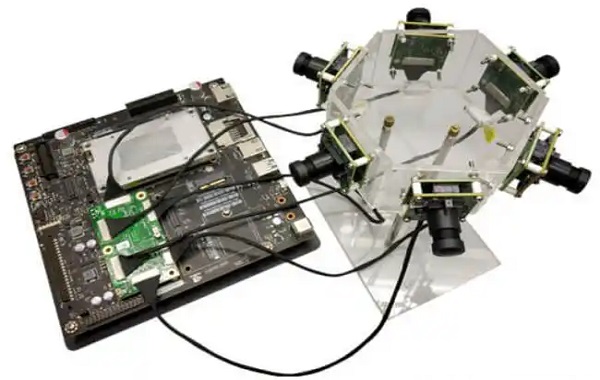
One, structural advantages and essential differences
The coaxial structure of extremely thin coaxial cables is composed of a central conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer, and outer sheath, which can effectively shield external electromagnetic interference and ensure stable transmission of high-speed signals. In comparison, FFC ribbon cables arrange multiple conductors in parallel on a flexible film, although they are cost-effective and easy to assemble, they lack an independent shielding layer and are susceptible to interference and crosstalk. It is evident that Micro Coax is more like a cable束 equipped with armor, while FFC is akin to bare wire arrangement. In high-speed signal transmission, this structural difference directly determines the performance limit.

Electrical Performance and High-Speed Transmission Ability
Micro Coax has significant advantages in electrical performance:
• Low signal attenuation: The design with a constant characteristic impedance ensures stable long-distance signal transmission.
• Strong anti-interference ability: The metal shielding layer blocks external electromagnetic waves and reduces crosstalk.
• Support high frequency: Can easily handle high-speed interfaces such as MIPI CSI, LVDS, V-by-One HS, up to several Gbps per second.
In contrast, the FFC wiring is prone to reflections, bit errors, and delays due to the lack of shielding and the parallel arrangement of conductors. Therefore, in NVIDIA's high-speed image transmission interfaces, Micro Coax has almost become the standard choice.

Three, mechanical characteristics and advantages of practical application
Extremely fine coaxial cable bundles not only transmit high-speed signals but also have excellent flexibility and bending resistance, maintaining stable performance even after tens of thousands of bends. They can be matched with miniature connectors (such as I-PEX, JAE, etc.) to achieve high-density, limited space connections, meeting the needs of high-reliability scenarios such as autonomous driving cameras, robot vision modules, and folding display devices. In comparison, FFC ribbon cables are prone to breakage after repeated bending, have insufficient reliability, and are not suitable for high-speed, long-distance, and high-interference environments.

The reason why NVIDIA recommends using extremely thin coaxial cable bundles is clear: in high-speed signal transmission, Micro Coax has better signal integrity, anti-interference capability, and mechanical reliability, while FFC ribbon cables are more suitable for low-speed, low-interference, and cost-sensitive scenarios. With the increasing bandwidth requirements for AI computing platforms, vehicle systems, and industrial vision applications, Micro Coax cable bundles will become the mainstream solution for high-speed interconnects.
I am
Suzhou Huichengyuan Electronic TechnologyLong-term focus on the design and customization of high-speed signal cables and ultra-thin coaxial cables, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnection solutions. If you have any needs or want to learn more, welcome to contact
Manager Zhang: 18913228573 (WeChat same number)。



