In today's rapidly developing era of high-speed signal transmission and equipment miniaturization, ultra-thin coaxial cable bundles (Micro Coaxial Cable) are widely used in fields such as smartphones, medical devices, drones, security monitoring, and vehicle systems, thanks to their high-frequency low-loss, excellent shielding performance, and flexibility. However, many engineers have found in practice that ultra-thin coaxial cable bundles often experience signal attenuation in high-frequency or long-distance transmission situations. So, what exactly is signal attenuation? And how can it be effectively addressed? This article will systematically analyze it for you.

What is signal attenuation?
Signal attenuation refers to the phenomenon of electronic signals gradually weakening during transmission.
In simple terms, it is that the signal "weakens as it is transmitted," resulting in the receiving end obtaining a signal strength lower than that of the sending end.
Attenuation is usually expressed in decibels (dB), with higher values indicating more severe signal loss.
In extremely thin coaxial cables, signal attenuation is an unavoidable physical characteristic, mainly affected by the following factors:
Transmission medium resistance loss
Electromagnetic radiation and signal leakage
Connector or junction impedance mismatch
External electromagnetic interference (EMI) influence
When the signal attenuation is too great, it can cause signal distortion, data errors, and even lead to communication interruption, seriously affecting the stability and reliability of the equipment.

Why does signal attenuation occur?
Main reasons for signal attenuation include the following:
Transmission distance too long: the finer the wire diameter, the greater the loss per unit length, and the more obvious the attenuation becomes the farther the distance.
High-frequency signal loss: High-frequency signals are more affected by "skin effect," with current concentrating on the surface of the conductor, while the surface area of a very thin conductor is limited, which is prone to cause energy loss.
Welding or connection quality issues: Solder joints and poorly contacting plug connectors can cause signal instability or loss.
External electromagnetic interference (EMI): Although the coaxial structure inherently has anti-interference capability, it may still affect signal quality in strong interference environments.
Cable bending or mechanical damage: Frequent bending or external force compression can damage the shielding layer or conductor structure, causing signal attenuation.
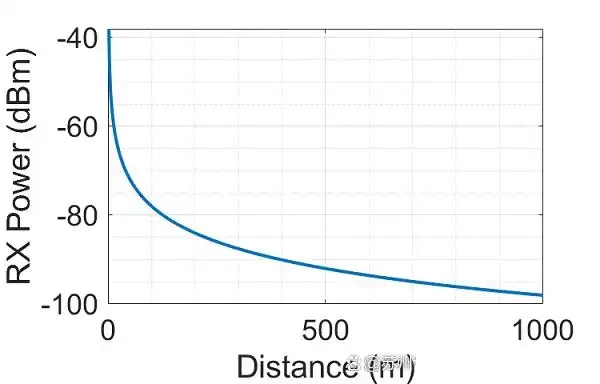
How to solve signal attenuation? Six optimization strategies
Optimize cable selection
Prioritize low-loss type, dual-shielded, or high-shielding density (≥90%) Micro Coaxial Cable.
Recommend using high-quality brand cables that have passed UL/ISO certification to ensure consistency and long-term stability.
Reasonably control the transmission distance
Minimize the cable length; if long-distance transmission is required by the system, a signal amplifier or repeater can be added for compensation.
Strict welding and assembly technology
Solder joints should be firm and reliable, without cold solder joints; the connectors should fit well.
It is recommended to use a dedicated Micro Coax stripping and welding fixture to improve joint consistency and signal integrity.
Strengthen EMI shielding measures
It is possible to add a metal mesh or aluminum foil shielding tube to the outer surface of the cable; at the same time, optimize the cable layout, keeping away from high-frequency and strong interference sources.
Prevent excessive cable bending
The reasonable bending radius should be controlled during design (usually ≥ 5 times the wire diameter), and cable fixing clamps should be used to prevent suspension, swinging, or pulling.
6. Perform Signal Integrity Testing
Test the signal strength before and after transmission using a TDR meter or a spectrum analyzer to promptly detect and correct potential issues.
Extremely thin coaxial cable bundles are known for their thinness, flexibility, and high-density connections, but their high-frequency long-distance transmission characteristics put higher requirements on signal quality. As long as systematic optimization is carried out in aspects such as selection, process, shielding, wiring, and testing, the problem of signal attenuation can be effectively controlled, helping equipment to achieve faster, more stable, and reliable signal transmission.
We have been focusing on the design and customization of high-speed signal cable harnesses and ultra-fine coaxial cable harnesses for a long time, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnect solutions. If you have any related needs or would like to learn more, please feel free to contact us:
Manager Zhang 18913228573 (WeChat same number).



