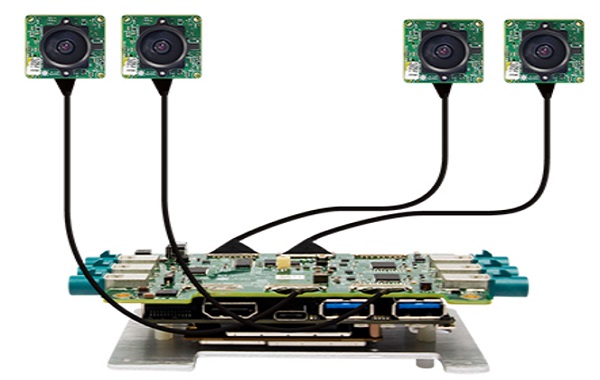
In smartphones, vehicle-mounted cameras, industrial vision systems, and VR/AR devices, the MIPI interface has gradually become the core standard for high-speed image and display transmission. With the continuous improvement of resolution, frame rate, and channel rate, high-speed signal chains place higher requirements on the cable's loss, crosstalk, anti-interference ability, and flexible structure. Against this backdrop, ultra-thin coaxial cables, with their precise coaxial structure, high bandwidth capability, and excellent shielding characteristics, have become the key connection solution for MIPI high-speed signal transmission.
This article will analyze how the ultra-thin coaxial cable束 meets the performance requirements of the MIPI high-speed link from three aspects: structural characteristics, transmission advantages, and design selection.
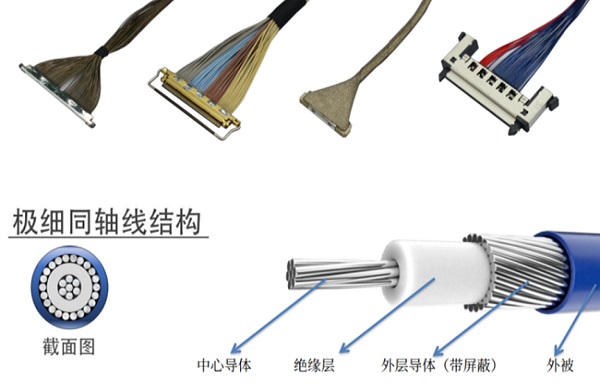
Structure and Performance Characteristics of Extremely Fine Coaxial Beam
Extremely thin coaxial cables achieve a highly integrated transmission channel through the center conductor, dielectric, metal shielding layer, and outer sheath, realizing miniaturization, low loss, and high shielding. Their typical diameter ranges between 0.2mm and 0.5mm, and are suitable for compact high-speed equipment. Their main performance is reflected in the following aspects:
Excellent shielding capability: The coaxial structure naturally has a 360-degree shielding effect, which can effectively suppress external interference and signal crosstalk.
Low loss, high bandwidth: By strictly controlling the conductor size and medium parameters, high impedance consistency and low insertion loss can be achieved, supporting high-speed transmission requirements of tens of GHz.
High flexibility and small volume: Suitable for wiring in limited space modularity, it can maintain extremely small bending radius while ensuring reliable contact.
It is easy to support high-speed differential signals: although MIPI uses differential transmission, the extremely thin coaxial structure can still achieve high-quality differential links through impedance control.
The core advantages in high-speed transmission of MIPI
MIPI interfaces (such as CSI-2, DSI) support D-PHY and C-PHY standards, with channel rates up to 1~6Gbps and even higher, demanding extremely high signal integrity for cables. The advantages of extremely thin coaxial cables in MIPI systems are reflected in:
High-speed and signal integrity performance are excellent: single-core impedance can be stabilized at 50Ω or differential 100Ω, significantly reducing reflection and echo loss, resulting in clear eye diagrams and low error rates.
The strong EMI suppression capability: The metal shielding layer and independent grounding design reduce high-frequency interference and strengthen the system's resistance to external interference.
High integration module: Thin and flexible structure can navigate around in narrow spaces, meeting the requirements of mobile phone cameras, VR modules, and automotive systems for volume and flexibility.
Excellent match with miniature high-speed connectors: Often used in conjunction with I-PEX, Hirose, JAE, and other connectors, it can provide high-speed connection effects with low reflection, high shielding, and reliable contact.

Key points of system design and selection
When using extremely thin coaxial cable bundles in MIPI high-speed links, it is necessary to comprehensively consider electrical, mechanical, and processing consistency factors to ensure stable operation:
Control the length of wiring harness: High-speed links should be kept as short as possible to reduce insertion loss and reflection risk.
Impedance consistency: Ensure the impedance continuity of the link from the camera module to the mainboard, avoiding sudden changes that may cause signal reflections.
3. Standardize bending radius: Follow the minimum bending radius requirements for cable harnesses to avoid excessive bending and resulting shielding damage.
Shielding and grounding: Use full shielding and multi-point grounding structures to enhance anti-interference ability.
Select connector matching: choose a miniature connector that supports high-speed differential signaling and ensure that the welding process is continuous with the signal path.
System-level verification: Confirm the stability and anti-interference performance of high-speed links through SI (Signal Integrity) and EMC tests.

As image and display resolutions continue to improve, the MIPI high-speed link imposes more stringent requirements on signal integrity and system structure. The extremely thin coaxial cable bundle, with its high bandwidth, low loss, strong anti-interference capability, and excellent spatial adaptability, has become the core interconnection solution for MIPI transmission. In the future high-resolution imaging, intelligent driving, industrial vision, and AR/VR systems, the extremely thin coaxial cable bundle will continue to play a significant role, providing a stable and reliable foundation for high-speed data links.
I am
[Suzhou Huichengyuan Electronic Technology]Long-term focus on the design and customization of high-speed cable harnesses and ultra-fine coaxial cable harnesses, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnection solutions. For inquiries or more information, please feel free to contact
Manager Zhang: 18913228573 (WeChat same number)。



